Win32/Conficker.AA also known W32/Worm.AHGV, Net-Worm.Win32.Kido.bg, Worm:Win32/Conficker, W32/Conficker.worm.gen, Mal/Conficker is a worm that uses Microsoft Windows Server Service RPC Handling Remote Code Execution Vulnerability (MS08-67) in order to spread on other computers in the local network. The worm blocks user access to security websites, deletes all the System Restore points prior to infection, protects itself from deletion by removing all NTFS file permissions,except execute and directory traversal and more. Starting in April 2009, this worm also installs Spyware Protect 2009.
Automated Removal Instructions for Conficker worm.
1. Download MS08-67 vulnerability patch, according to your Windows version, from here.
2. Install MS08-67 vulnerability patch.
3. Download Win32.Worm.Downadup.Gen (Win32/Conficker.AA) removal tool by BitDefender from here.
4. Unzip/extract it to a folder on your desktop.
5. Unplug network cable.
6. Open folder and you will now see an icon on your desktop similar to the one below.
![]()
Anti-Downadup-graphics (WormW32Downadup.AL removal tool) icon
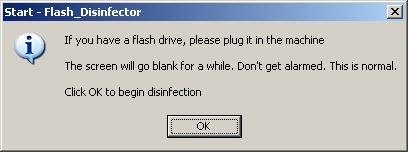
7. Double click to Anti-Downadup-graphics icon to run it and you will see a prompt similar to the figure below.
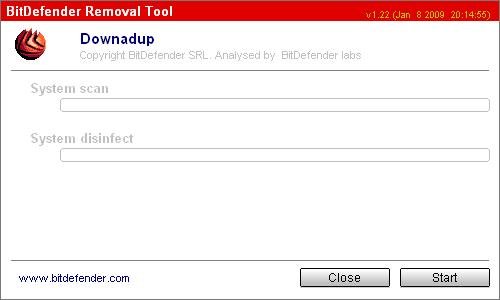
WormW32Downadup.AL removal tool main window
8. Click Start button.
9. Reboot your computer when done.
10. Plug in your network cable.
11. Make a new restore point.
- Disable system restore to flush out infected restore points.
- Reboot your computer again.
- Turn on Windows System Restore.
- Click START -> ALL PROGRAMS -> ACCESSORIES -> SYSTEM TOOLS -> SYSTEM RESTORE.
- Click on “create new restore point”, then click on NEXT and follow the prompts.
Manual Removal Instructions for Conficker worm
Click here for read Microsoft Knowledge Base Article 962007 provides numerous details for manual disinfection.
Note: if you need help with the instructions, then post your questions in our Spyware Removal forum.





Thanks
That’s what I’m waiting for..
I am probably infected with Win32/Conficker.AA. ((All symptoms, even the one that is sending stuff and strange advertissement with my mails) :I was glad to find your removal tool, but the first step of your kit is refering to the MICROSOFT SECURITY CENTER THE WORM PROHIBITS THE ACCESS (SEE YOUR DESCRIPTION).So you should offeranother more realistic solution….Offering to download the patch from a NOT recognised security webpage….
You should use another computer for download MS patch and worm removal tool.
to be able to access the microsoft website just Stop/Start the DNS Service. The worm mangles with DNS only at the bootup. So Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Services > DNS Client.
Stop and Start the DNS and you will be able to access the M$ website.
a great day,
v
PS: thanks for the removal tool
Hello Patrick and v,
unfortunately it did not work, but I am happy to see that other people are trying to help….Tx.
I used another computer Ihad installed with XP, but that did not run since one year,…, so Ihad first to update (That worked – carefully) and I put one free antivirus. At the end of the day Icould download the Patch into a Flash….Installed with the Bitdef tool (He is givingthe indication that everithyng is OK and did NOT desinfect. Aat the End but, nothing. I also use the v solution but I do not know…(It was so simple) nthing happened….May be someone has anothe idea…
Tx to all
Philippe
Try another free cleaning tool available from F-Secure http://www.f-secure.com/v-descs/worm_w32_downadup_al.shtml
Until I get all my computers updated and cleaned I\’m using a PowerShell script to unlock the AD users. I get a list of user and create a script running this command:
Unlock-QADUser user_name
The ActiveRoles Management Shell for Active Directory is required to execute the command above
http://www.quest.com/powershell/activeroles-server.aspx
New free cleaning tool available from Kaspersky Lab.
1. Download the tool (klwk.zip) from here http://data2.kaspersky-labs.com:8080/special/klwk.zip
2. Extract the contents into a folder on the infected PC.
3. Run file run_klwk.bat
4. Wait till the scanning is complete.
Article ID: 962007 – Last Review: January 15, 2009 – Revision: 2.1
Virus alert about the Win32/Conficker.B worm
If your computer is infected with this worm, you may not experience any symptoms, or you may experience any of the following symptoms:
Account lockout policies are being tripped.
Automatic Updates, Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS), Windows Defender, and Error Reporting Services are disabled.
Domain controllers respond slowly to client requests.
The network is congested.
Various security-related Web sites cannot be accessed.
Propagation methods:
Win32/Conficker.B has multiple propagation methods. These include the following:
Exploitation of the vulnerability that is patched by security update 958644 (MS08-067)
The use of network shares
The use of AutoPlay functionality
Manual steps to remove the Conficker.b variant
The following detailed steps can help you manually remove Conficker.b from a system:
Log on to the system by using a local account.
Important Do not log on to the system by using a Domain account, if it is possible. Especially, do not log on by using a Domain Admin account. The malware impersonates the logged on user and accesses network resources by using the logged on user credentials. This behavior allows the malware to spread.
Stop the Server service. This removes the Admin shares from the system so that the malware cannot spread by using this method.
Note The Server service should only be disabled temporarily while you clean up the malware in your environment. This is especially true on production servers because this step will affect network resource availability. As soon as the environment is cleaned up, the Server service can be re-enabled.
To stop the Server service, use the Services Microsoft Management Console (MMC). To do this, follow these steps:
Depending on your system, do the following:
In Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008, click Start, type services.msc in the Start Search box, and then click services.msc in the Programs list.
In Windows 2000, Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003, click Start, click Run, type services.msc, and then click OK.
Double-click Server.
Click Stop.
Select Disabled in the Startup type box.
Click Apply.
Stop the Task Scheduler service.
To stop the Task Scheduler service in Windows 2000, Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003, use the Services Microsoft Management Console (MMC) or the SC.exe utility.
To stop the Task Scheduler service in Windows Vista or in Windows Server 2008, follow these steps.
Important This section, method, or task contains steps that tell you how to modify the registry. However, serious problems might occur if you modify the registry incorrectly. Therefore, make sure that you follow these steps carefully. For added protection, back up the registry before you modify it. Then, you can restore the registry if a problem occurs. For more information about how to back up and restore the registry, click the following article number to view the article in the Microsoft Knowledge Base:
322756 (http://support.microsoft.com/kb/322756/ ) How to back up and restore the registry in Windows
Click Start, type regedit in the Start Search box, and then click regedit.exe in the Programs list.
Locate and then click the following registry subkey:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Schedule
In the details pane, right-click the Start DWORD entry, and then click Modify.
In the Value data box, type 4, and then click OK.
Exit Registry Editor, and then restart the computer.
Download and manually install security update 958644 (MS08-067). For more information, visit the following Microsoft Web site:
http://www.microsoft.com/technet/security/Bulletin/MS08-067.mspx (http://www.microsoft.com/technet/security/Bulletin/MS08-067.mspx)
Note This site may be blocked because of the malware infection. In this scenario, you must download the update from an uninfected computer, and then transfer the update file to the infected system. We recommend that you burn the update to a CD because the burned CD is not writable. Therefore, it cannot be infected. If a recordable CD drive is not available, a removable USB memory drive may be the only way to copy the update to the infected system. If you use a removable drive, be aware that the malware can infect the drive with an Autorun.inf file. After you copy the update to the removable drive, make sure that you change the drive to read-only mode, if the option is available for your device. If read-only mode is available, it is typically enabled by using a physical switch on the device. Then, after you copy the update file to the infected computer, check the removable drive to see whether an Autorun.inf file was written to the drive. If it was, rename the Autorun.inf file to something like Autorun.bad so that it cannot run when the removable drive is connected to a computer.
Reset any Local Admin and Domain Admin passwords to use a new strong password. For more information, visit the following Microsoft Web site:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc875814.aspx (http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc875814.aspx)
In Registry Editor, locate and then click the following registry subkey:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\SvcHost
In the details pane, right-click the netsvcs entry, and then click Modify.
Scroll down to the bottom of the list. If the computer is infected with Conficker.b, a random service name will be listed. For example, in this procedure, we will assume the name of the malware service is “gzqmiijz”. Note the name of the malware service. You will need this information later in this procedure.
Delete the line that contains the reference to the malware service. Make sure that you leave a blank line feed under the last legitimate entry that is listed, and then click OK.
Note All the entries in the following list are valid. Do not delete any of these entries. The entry that must be deleted will be a randomly generated name that is the last entry in the list.
AppMgmt
AudioSrv
Browser
CryptSvc
DMServer
EventSystem
HidServ
Ias
Iprip
Irmon
LanmanServer
LanmanWorkstation
Messenger
Netman
Nla
Ntmssvc
NWCWorkstation
Nwsapagent
Rasauto
Rasman
Remoteaccess
Sacsvr
Schedule
Seclogon
SENS
Sharedaccess
Themes
TrkWks
TrkSvr
W32Time
WZCSVC
Wmi
WmdmPmSp
winmgmt
wuauserv
BITS
ShellHWDetection
uploadmgr
WmdmPmSN
xmlprov
AeLookupSvc
helpsvc
axyczbfsetg
Restrict permissions on the SVCHOST registry key so that it cannot be written to again. To do this, follow these steps.
Notes
You must restore the default permissions after the environment has been fully cleaned.
In Windows 2000, you must use Regedt32 to set registry permissions.
In Registry Editor, locate and then click the following registry subkey:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Svchost
Right-click the Svchost subkey, and then click Permissions.
In the Permissions Entry for SvcHost dialog box, click Advanced.
In the Advanced dialog box, click Add.
In the Select User, Computer or Group dialog box, type everyone, and then click Check Names.
Click OK.
In the Permissions Entry for SvcHost dialog box, select This key only in the Apply onto list, and then click to select the Deny check box for the Set Value permission entry.
Click OK two times.
Click Yes when you receive the Security warning prompt.
Click OK.
In a previous procedure, you noted the name of the malware service. In our example, the name of the malware entry was “gzqmiijz”. Using this information, follow these steps:
In Registry Editor, locate and then click the following registry subkey, where BadServiceName is the name of the malware service:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\BadServiceName
For example, locate and then click the following registry subkey:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\gzqmiijz
Right-click the subkey in the navigation pane for the malware service name, and then click Permissions.
In the Permissions Entry for SvcHost dialog box, click Advanced.
In the Advanced Security Settings dialog box, click to select both of the following check boxes:
Inherit from parent the permission entries that apply to child objects. Include these with entries explicitly defined here.
Replace permission entries on all child objects with entries shown here that apply to child objects
Press F5 to update Registry Editor. In the details pane, you can now see and edit the malware DLL that loads as “ServiceDll” To do this, follow these steps:
Double-click the ServiceDll entry.
Note the path of the referenced DLL. You will need this information later in this procedure. For example, the path of the referenced DLL may resemble the following:
%SystemRoot%\System32\emzlqqd.dll
Rename the reference to resemble the following:
%SystemRoot%\System32\emzlqqd.old
Click OK.
Remove the malware service entry from the Run subkey in the registry.
In Registry Editor, locate and then click the following registry subkeys:
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
In both subkeys, locate any entry that begins with “rundll32.exe” and also references the malware DLL that loads as “ServiceDll” that you identified in step 12b. Delete the entry.
Exit Registry Editor, and then restart the computer.
Check for Autorun.inf files on any drives on the system. Use Notepad to open each file, and then verify that is a valid Autorun.inf file. The following is an example of a typical valid Autorun.inf file.
[autorun]
shellexecute=Servers\splash.hta *DVD*
icon=Servers\autorun.ico
A valid Autorun.inf is typically 1 to 2 kilobytes (KB).
Delete any Autorun.inf files that do not seem to be valid.
Restart the computer.
Make hidden files visible. To do this, type the following command at a command prompt:
reg.exe add HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Advanced\Folder\Hidden\SHOWALL /v CheckedValue /t REG_DWORD /d 0x1 /f
Set Show hidden files and folders so you can see the file. To do this, follow these steps:
In step 12b, you noted the path of the referenced DLL file for the malware. For example, you noted a path that resembles the following:
%systemroot%\System32\emzlqqd.dll
In Windows Explorer, open the %systemroot%\System32 directory, or the directory that contains the malware.
Click Tools, and then click Folder Options.
Click the View tab.
Select the Show hidden files and folders check box.
Click OK.
Select the DLL file.
Edit the permissions on the file to add Full Control for Everyone. To do this, follow these steps:
Right-click the DLL file, and then click Properties.
Click the Security tab.
Click Everyone, and then click to select the Full Control check box in the Allow column.
Click OK.
Delete the referenced DLL file for the malware. For example, delete the %systemroot%\System32\emzlqqd.dll file.
Remove all AT-created scheduled tasks. To do this, type AT /Delete /Yes at a command prompt.
Enable the BITS, Automatic Updates, Error Reporting, and Windows Defender services by using the Services Microsoft Management Console (MMC).
Turn off Autorun to help reduce the effect of any reinfection. To do this, follow these steps:
Depending on your system, install one of the following updates:
If you are running Windows 2000, Windows XP, or Windows Server 2003, install update 953252. For more information, click the following article number to view the article in the Microsoft Knowledge Base:
953252 (http://support.microsoft.com/kb/953252/ ) How to correct “disable Autorun registry key” enforcement in Windows
If you are running Windows Vista or Windows Server 2008, install security update 950582. For more information, click the following article number to view the article in the Microsoft Knowledge Base:
950582 (http://support.microsoft.com/kb/950582/ ) MS08-038: Vulnerability in Windows Explorer could allow remote code execution
Note Update 953252 and security update 950582 are not related to this malware issue. These updates must be installed to enable the registry function in step 23b.
Type the following command at a command prompt:
reg.exe add HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\Explorer /v NoDriveTypeAutoRun /t REG_DWORD /d 0xff /f
If the system is running Windows Defender, re-enable the Windows Defender autostart location. To do this, type the following command at the command prompt:
reg.exe add HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run /v “Windows Defender” /t REG_EXPAND_SZ /d “%ProgramFiles%\Windows Defender\MSASCui.exe –hide” /f
For Windows Vista and later operating systems, the malware changes the global setting for TCP Receive Window Auto-tuning to disabled. To change this setting back, type the following command at a command prompt:
netsh interface tcp set global autotuning=normal
If, after you complete this procedure, the computer seems to be reinfected, either of the following conditions may be true:
One of the autostart locations was not removed. For example, either the AT job was not removed, or an Autorun.inf file was not removed.
The security update for MS08-067 was installed incorrectly
This malware may change other settings that are not addressed in this Knowledge Base article. Please visit the following Microsoft Malware Protection Center Web page for the latest details about Win32/Conficker.b:
http://www.microsoft.com/security/portal/Entry.aspx?Name=Win32/Conficker (http://www.microsoft.com/security/portal/Entry.aspx?Name=Win32/Conficker)
Back to the top
Verify that the system is clean
Verify that the following services are started:
Automatic Updates (wuauserv)
Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS)
Windows Defender (windefend) (if applicable)
Windows Error Reporting Service
To do this, type the following commands at the command prompt. Press ENTER after each command:
Sc.exe query wuauserv
Sc.exe query bits
Sc.exe query windefend
Sc.exe query ersvc
After each command runs, you will receive a message that resembles the following:
SERVICE_NAME: wuauserv
TYPE : 20 WIN32_SHARE_PROCESS
STATE : 4 RUNNING
(STOPPABLE,NOT_PAUSABLE,ACCEPTS_SHUTDOWN)
WIN32_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0)
SERVICE_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0)
CHECKPOINT : 0x0
WAIT_HINT : 0x0
In this example, “STATE : 4 RUNNING” indicates that the service is running.
To verify the status of the SvcHost registry subkey, follow these steps:
In Registry Editor, locate and then click the following registry subkey:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\SvcHost
In the details pane, double-click netsvcs, and then review the service names that are listed. Scroll down to the bottom of the list. If the computer is reinfected with Conficker.b, a random service name will be listed. For example, in this procedure, the name of the malware service is “gzqmiijz”.
If these steps do not resolve the issue, contact your antivirus software vendor. For more information about this issue, click the following article number to view the article in the Microsoft Knowledge Base:
49500 (http://support.microsoft.com/kb/49500/ ) List of antivirus software vendors
If you do not have an antivirus software vendor, or your antivirus software vendor cannot help, contact Microsoft Consumer Support Services for more help.
Back to the top
After the environment is fully cleaned
After the environment is fully cleaned, do the following:
Re-enable the Server service.
Restore the default permissions on the SVCHOST registry key.
Update the computer by installing any missing security updates. To do this, use Windows Update, Microsoft Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) server, Systems Management Server (SMS), System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM), or your third-party update management product. If you use SMS or SCCM, you must first re-enable the Server service. Otherwise, SMS or SCCM may be unable to update the system.
Hi all,
Can anyone tell me if any of the removal tools mentioned above will work on NT4?
Thanks in advance.
LeeH, no 100%, but try it.
IT WORKS BABY!!! THANKS….
It also works for me. Thanks so much!
How delete conficker aa
If these instructions have not helped you, then please follow these steps.
GOD BLESS bitdefender!!! MSRT and other tools would not detect this virus. Manual instruction also did not help me!
I finally ran this tool and it got rid of conficker.b.
THANK YOU
Conficker manual removal steps are given on my blog.. Those who like to get the thrill of doing it yourself can do so check out digitalpbk.blogspot.com/2009/04/jwgkvsqvmx-conficker-virus-manual.html
thank’s for you articles
Thanks for sharing this post.
What worked for me:
1.Pres Win Key + R
2.The Run dialog will appear
3.type services.msc
4.Find the following services and perform the actions pointed
a)DNS Client -> Right mouse button, Properties, Click Stop, in Startup Type drop down choose Disabled, Click OK
b)Background Intelligent Transfer Service -> Right mouse button, Properties, in Startup Type drop down choose Automatic, Click OK
b)Automatic Updates -> Right mouse button, Properties, in Startup Type drop down choose Automatic, Click OK
5.Now Go to Start>Control Panel>Automatic Updates and change to Notify me for updates , but do not download them(or if this is chosen use the other one – to download, but without installing)
6.Wait for notification that the updates are ready – at leas Microsoft Malicious software removal tool for January should be there.
7.Install all of them and restart as many times, as necessary.
8.After the last restart it should report that had removed the Conflicker worm of some kind.Click OK on that dialog
9.Re-enable the DNS Client service now using the steps from 1 to 4
You must be done by then
I have a problem my gf got this trojan from usb today atleast i think its this one, now she doesnt have access to windows, i wonder if running computer in safe mode and cleaning it with troyan remower would help simplysup.com/tremover/details.html
the thing is that i dont have it jet installed and would probably have to install it in safe mode
if trojan remower wouldnt help id try icrosoft Malicious software removal tool, i wonder if this problem can be handled this way, thanks